Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process
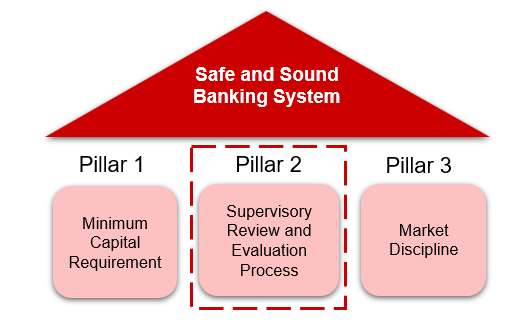
ICAAP (Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process), part of Pillar 2 within the Basel Framework, represents a financial institution's own assessment of the capital needed to run the business
Become compliant with the requirements of Ind AS 116 / IFRS 16 using the cloud-based software tool used by several corporate entities
Schedule an Intro Call
Enter your info and we'll show you calendar options to meet with a member of our team:
What are the requirements for ICAAP?
Summary of the key requirements of ICAAP as prescribed by the RBI:
Board and Senior Management Oversight: The Board of Directors and senior management are primarily responsible for understanding the nature and the level of risk taken by the bank. They must ensure that the bank has the capability to manage these risks effectively.
Capital Adequacy Policy: Banks should have in place a well-defined capital adequacy policy that articulates their approach to capital management. This should be reviewed periodically.
Risk Identification: Banks must have a process that allows for identification of material risks, both current and potential.
Measurement Techniques: Institutions must have sound methodologies in place to measure the various risks they're exposed to. These might include credit risk, market risk, operational risk, liquidity risk, interest rate risk in the banking book, and other relevant risks.
Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis: Banks must conduct stress tests to assess potential vulnerabilities under extreme but plausible adverse conditions. These tests should span various time horizons and consider both short-term and protracted crises.
Setting and Review of Capital Targets: Banks should set internal targets for capital that are commensurate with their risk profile and control environment. These targets should be reviewed regularly.
Strategies for Maintaining Capital: Banks should have strategies in place for addressing potential capital shortfalls.
Ensuring Capital Compliance: Banks need to monitor and ensure that they meet regulatory and internal capital targets. They should have early warning mechanisms in place to alert management if they are at risk of breaching these limits.
Feedback Loop: There should be a feedback loop between the bank's capital assessment process and its risk and capital management processes. This ensures that the ICAAP remains dynamic and adjusts to the changing risk profile of the bank.
Documentation and Reporting: Banks should have a well-documented ICAAP that clearly articulates their risk management and capital assessment methodologies. They should also have in place a mechanism for periodic reporting to the Board and senior management on the bank's risk profile and capital needs.
Review by Supervisors: The RBI or other designated authorities will review the ICAAP as part of the supervisory process. Banks are expected to provide any information requested by the supervisor and must be able to demonstrate the soundness of their processes.
Internal Audit Review: The bank's internal audit function should review the ICAAP to ensure its effectiveness and compliance with internal policies and regulatory guidelines.
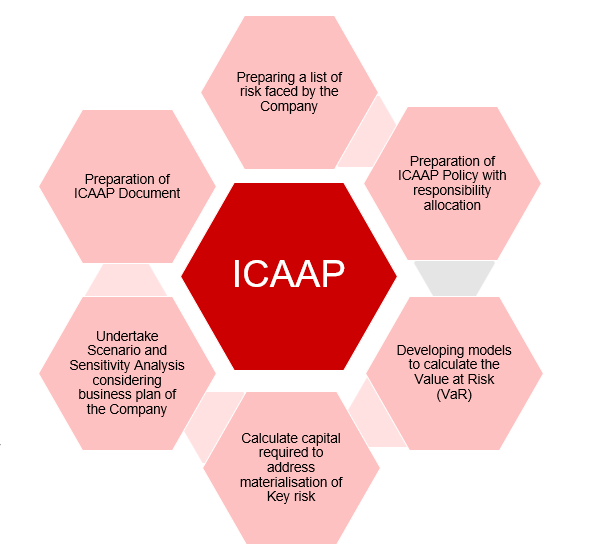
RVSBELL Analytics would provide the summarised process in the ICAAP document to be reviewed by board and submitted to RBI
Financial Institutions must demonstrate to the regulators that they have implemented methods and procedures to ensure adequate capital resources, with due attention to all material risk. - sufficiency of “Economic Capital”
Talk To An ExpertApproach to ICAAP
The Methodology would be developed after considering current governance structure of the Company specifically risk management function
The business model of Company for the purpose of ICAAP can be categorised into “Simple” “Moderately Complex” or “Complex”.
We shall assist the Company in determining the complexity level for its operations, and accordingly align the ICAAP approach.
The business model of Company for the purpose of ICAAP can be categorised into “Simple” “Moderately Complex” or “Complex”.
We shall assist the Company in determining the complexity level for its operations, and accordingly align the ICAAP approach.

Factors considered in capital requirements
Significant factors in capital requirements include:
Future capital needs, in line with the business projections of the Company.
We will take a minimum 3 – 5 years horizon. Expected and unexpected losses in view of concentricity, correlation, probability of default, business cycle etc.
Strains on liquidity, with stress on cash inflows from receivables, cash outflows from liabilities prone to early payment, etc.
We will take a minimum 3 – 5 years horizon. Expected and unexpected losses in view of concentricity, correlation, probability of default, business cycle etc.
Strains on liquidity, with stress on cash inflows from receivables, cash outflows from liabilities prone to early payment, etc.
Economic and stress testing models
The econometric and stress testing models shall be developed for each quantifiable risks to determine the VaR and Capital Requirement. The models developed would be based on current practices of the Company
Policy with appropriate responsibility allocation shall be drafted.
A draft ICAAP document shall be drafted, mentioning key outcomes considering first ICAAP analysis.

Road Map and Knowledge Transfer for Implementation
Assisting Senior Management and Risk Team in implementation of the ICAAP framework
Holding a meeting to apprise the relevant team on the complete structure of ICAAP
Addressing any queries in respect to ICAAP implementation
Assist in development of Appropriate MIS for ICAAP framework
Holding a meeting to apprise the relevant team on the complete structure of ICAAP
Addressing any queries in respect to ICAAP implementation
Assist in development of Appropriate MIS for ICAAP framework