Mutual Agreement Procedure
- Mutual Agreement Procedure (‘MAP’) is a procedure set out in most treaties which permit designated Government representatives to work together to resolve international tax disputes including issues involving double taxation, questions regarding residential status, tax recovery etc.
- MAP is used to eliminate double taxation that can arise from transfer pricing adjustments.
Eligibility for MAP
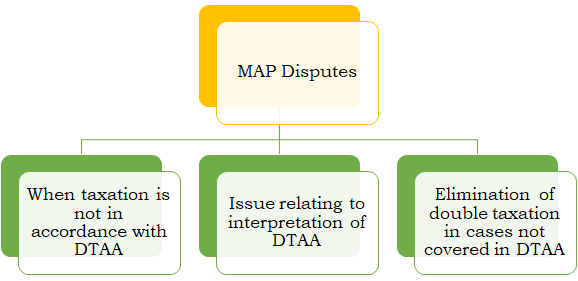
- MAP application can be filed by a person when he considers that he has not been taxed in accordance with the Treaty.
- Even if such person has other remedies such as appeal process under the domestic laws, MAP can be initiated. MAP can be applied in the country in which he is a resident or a national.
- This can be presented within three years from the date of receipt of notice of the action which gives rise to taxation not in accordance with convention.
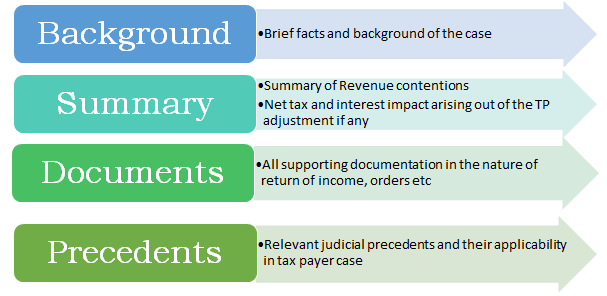
Steps in MAP application
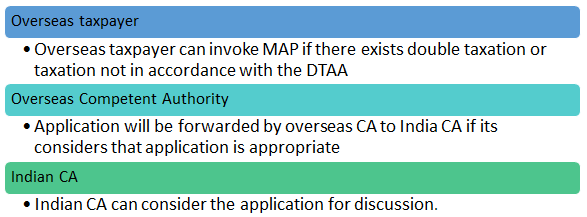
MAP process in India

Drawbacks of MAP

Income from transaction with Non-Residents – Transfer Pricing
Transfer pricing adjustment and consequence
Dispute Mitigation strategies in transfer pricing
Advance Pricing Agreements (APA)
Fundamentals of Base Erosion and Profit Shifting – Transfer Pricing
Anti-Avoidance measures in certain jurisdictions – Transfer pricing
Returns, Audit and other miscellaneous provisions – Transfer pricing
Determination of ALP – Transfer Pricing
Arm’s Length Principle – Transfer Pricing
Specified Domestic Transactions – Transfer Pricing
Secondary Adjustment – transfer pricing
International Transaction [Section 92B] – Transfer Pricing
Additional reporting by Multinational companies – Transfer pricing
Economic analysis – Transfer Pricing
Limitation of interest deductions – transfer pricing
Penalties for non-compliance – Transfer Pricing